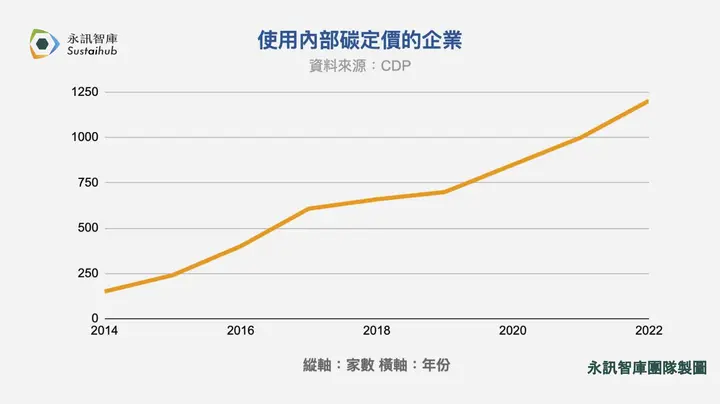
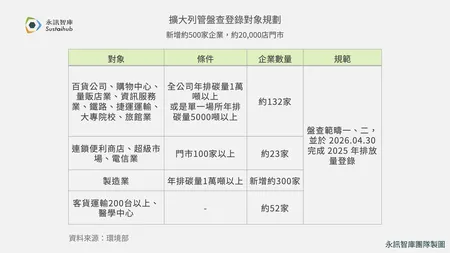
What is Internal Carbon Pricing?
Internal carbon pricing is an internal management tool that internalizes the cost of carbon emissions. This pricing mechanism typically assigns an economic value to each unit of carbon emission, enabling businesses to consider the cost of carbon emissions when making decisions. The purpose of internal carbon pricing is to encourage businesses to reduce carbon emissions during their operations and drive the transition to a low-carbon economy.
This tool has a wide range of applications, covering everything from product design and supply chain management to capital expenditure. By setting an internal carbon price, businesses can ensure that each department considers the impact of carbon emissions in their operational activities, thereby achieving overall emission reduction goals. Internal carbon pricing is not just an environmental measure but also a risk management strategy for businesses facing climate change risks.
There are various ways to implement internal carbon pricing, including shadow pricing, internal taxes, and carbon funds.
- Shadow pricing is a hypothetical price that businesses include in their decision-making considerations without actually charging externally.
- Internal carbon fees are charges levied by businesses on their departments or business units for carbon emissions. These funds can be used to support corporate sustainable development projects.
- Carbon funds involve businesses investing a certain amount of money into funds specifically dedicated to carbon reduction, supporting internal or external decarbonization projects.
What Are the Main Advantages of Internal Carbon Pricing?
Internal carbon pricing can bring multiple advantages to businesses. First, it can enhance a company's risk management capabilities. As global attention to climate change increases, government and market requirements for carbon emissions are becoming stricter, and the compliance and market risks faced by businesses are also increasing. Through internal carbon pricing, businesses can adapt to these changes in advance and reduce potential risks.
Second, internal carbon pricing helps promote innovation and enhance competitiveness. When carbon emissions are assigned economic value, businesses are more motivated to find ways to reduce carbon emissions. This not only helps businesses reduce operating costs but also drives technological innovation and opens up new market opportunities. For example, by improving energy efficiency or developing low-carbon products, businesses can gain competitive advantages in the market.
Additionally, internal carbon pricing helps improve corporate reputation. In today's society, consumers and investors increasingly value corporate sustainability performance. Businesses that actively take measures to reduce carbon emissions are more likely to win consumer favor and investor trust, thereby establishing a good brand image in the market and gaining long-term competitive advantages.
What Changes Occur in Businesses After Implementing Internal Carbon Pricing?
Internal carbon pricing has multifaceted impacts on businesses. First, it can influence corporate decision-making processes. By internalizing the cost of carbon emissions, businesses will more carefully consider the impact of carbon emissions when making decisions about capital expenditure, product design, supply chain management, etc., thereby making more sustainable decisions.
Second, internal carbon pricing can change how businesses operate. After implementing internal carbon pricing, businesses will pay more attention to energy efficiency and resource utilization, thereby optimizing their operational processes. For example, businesses may invest in more efficient production equipment to reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs. At the same time, businesses will actively seek opportunities to use renewable energy and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
Additionally, internal carbon pricing can promote cultural change within businesses. When carbon emissions are assigned economic value, employees will pay more attention to environmental protection and sustainable development. In such a cultural atmosphere, employees will be more motivated to find ways to reduce carbon emissions and actively participate in corporate sustainable development projects, thereby achieving company-wide emission reduction goals.
Challenges of Implementing Internal Carbon Pricing
Despite its many advantages, businesses face a series of challenges when implementing internal carbon pricing. First is internal resistance. When businesses promote internal carbon pricing, they may encounter resistance from different departments and employees. They may view it as an additional burden that increases workload and operating costs, thereby affecting company profits.
Second is the resource allocation issue. Implementing internal carbon pricing requires extensive data support, including measuring, analyzing, and reporting carbon emission data. This requires businesses to invest significant human and financial resources, which is a considerable challenge especially for smaller businesses with limited resources.
Finally, there is market volatility. Carbon emission prices are affected by market supply and demand relationships and policies between countries, and may fluctuate significantly. This creates uncertainty for businesses, affecting their long-term planning and decisions. For example, a sudden increase in carbon prices may increase a company's operating costs, thereby affecting its competitiveness and market share. Therefore, businesses implementing internal carbon pricing need to be prepared to deal with market volatility.
How to Develop an Effective Internal Carbon Pricing Strategy?
To develop an effective internal carbon pricing strategy, businesses first need to understand their current carbon emission status. Businesses should conduct a comprehensive carbon emission inventory to understand their carbon emissions during production and operations and identify the main sources of carbon emissions. This helps businesses develop targeted emission reduction measures and improve the effectiveness of internal carbon pricing.
Second, businesses should set a reasonable internal carbon price. This price should reflect the true cost of carbon emissions while not putting excessive pressure on business operations. Businesses can refer to market carbon prices, combined with their actual situation, to set a reasonable internal carbon price and regularly adjust it based on market changes and their own emission reduction goals.
Additionally, businesses should establish a comprehensive internal carbon pricing management system. This includes developing clear internal carbon pricing operational procedures, establishing carbon emission data management systems, and setting up dedicated carbon management departments. These measures help businesses improve the execution efficiency of internal carbon pricing and ensure it can truly work.
Microsoft and Shell Are Doing It! Internal Carbon Pricing Case Studies
Globally, many companies have successfully implemented internal carbon pricing and achieved significant results. For example, Microsoft has implemented internal carbon pricing since 2012, using the collected carbon fees to support its emission reduction projects worldwide. These revenues are used to procure renewable energy, support carbon removal plans, and improve data center energy efficiency. Through this mechanism, Microsoft not only became carbon neutral first but also announced in 2020 that it would achieve "carbon negative" by 2030.
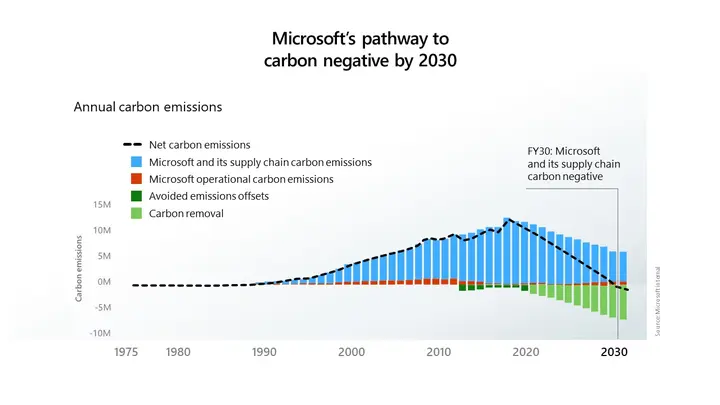
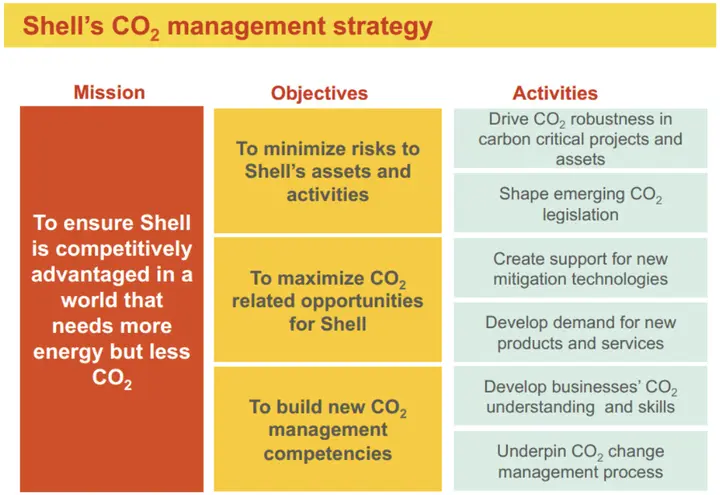
Another successful case is Shell, which has implemented internal carbon pricing since 2000, with prices ranging from $40 to $80 per ton of carbon dioxide. This influences investment decisions and promotes the development of low-carbon technologies such as carbon capture, natural gas, and biofuels. Between 2015 and 2016, direct emissions decreased by 2 million tons of carbon dioxide equivalent, showing that internal carbon pricing can effectively reduce emissions and promote sustainable strategies.
The Connection Between Internal Carbon Pricing and Corporate Sustainability Goals
Internal carbon pricing is closely related to corporate sustainability goals. Through internal carbon pricing, businesses can better manage their carbon emissions, achieve emission reduction goals, and thereby drive sustainable development. Internal carbon pricing can encourage businesses to pay more attention to environmental protection during their operations, reduce their environmental impact, and achieve a win-win for economic and environmental benefits.
Internal carbon pricing can also help businesses achieve their corporate social responsibility goals. In today's society, consumers and investors increasingly value corporate social responsibility performance. Businesses that actively take measures to reduce carbon emissions are more likely to win consumer favor and investor trust, thereby establishing a good brand image in the market and gaining long-term competitive advantages.
Additionally, internal carbon pricing can promote corporate innovation and development. When carbon emissions are assigned economic value, businesses will be more motivated to find ways to reduce carbon emissions, thereby driving technological innovation and opening up new market opportunities. For example, by improving energy efficiency or developing low-carbon products, businesses can gain competitive advantages in the market and achieve sustainable development.
Future Trends of Internal Carbon Pricing
As global attention to climate change continues to increase, the application of internal carbon pricing will become more widespread. In the future, more businesses will adopt internal carbon pricing as an important tool for sustainable development. This will encourage businesses to pay more attention to carbon emission management during their operations and drive the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Additionally, the calculation methods and management approaches for internal carbon pricing will become more refined. As technology advances and data becomes more abundant, businesses will be able to measure and analyze their carbon emission data more accurately, thereby developing more precise and effective internal carbon pricing strategies. For example, the application of AI and big data technology will improve the accuracy of carbon emission data and management efficiency, promoting the implementation of internal carbon pricing.
In the future, internal carbon pricing will also be combined with other sustainable development measures to form a comprehensive carbon management system. For example, businesses can combine internal carbon pricing with green supply chain management, renewable energy use, and other measures to form a comprehensive emission reduction strategy and achieve more efficient sustainable development goals.
Start Building Your Internal Carbon Pricing Blueprint Now
Internal carbon pricing, as an important tool for businesses to achieve sustainable development, has significant advantages and potential. Through internal carbon pricing, businesses can enhance risk management capabilities, promote innovation and competitiveness, and improve corporate reputation. However, businesses also face challenges such as internal resistance, resource allocation, and market volatility when implementing internal carbon pricing.
To overcome these challenges, businesses should conduct a comprehensive carbon inventory to understand their current carbon emission status before setting a reasonable internal carbon price and establishing a comprehensive internal carbon pricing management system. Additionally, businesses should actively learn from and draw on the successful experiences of other businesses to develop targeted internal carbon pricing strategies and ensure they can truly work.
DCarbon Cloud Carbon System: Digital Solution for Corporate Carbon Inventory, Complete from Inventory to Decarbonization!
DCarbon is a cloud-based greenhouse gas inventory system designed specifically for businesses, supporting cross-site data integration. Six steps can quickly complete carbon inventory ledgers and report generation. The system has built-in visual emission charts and carbon reduction pathway analysis, helping businesses fully grasp carbon emission hotspots and precisely plan carbon reduction actions, making the journey from inventory to net-zero easier.
🌱 Why Choose DCarbon?
One-stop Management: Integrate emission data from various sites, facilitating centralized management and setting carbon reduction goals
Intelligent Calculation Engine: Automatically convert emission quantities, reducing human error and operation time
Visual Presentation: Clear charted carbon emission pathways help you quickly identify hotspots and key carbon reduction actions
📌 Start Using Now Try DCarbon System Now
References
Center for Climate and Energy Solutions - Companies Set Their Own Carbon Price Report
Skeptical Science - Shell Internal Carbon Pricing Analysis
Companies setting their own carbon prices without global standard: Reuters | ESG Dive
Microsoft Sustainability Reports (2020–2024)
Publication: State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2023