Why is ESG Disclosure Important?
In recent years, enterprises have been constantly hearing about "ESG, sustainability disclosure, sustainability reports, and carbon inventory." As voluntary disclosure gradually transitions to mandatory regulations, many companies still ask internally:
"Why do we really need to do this?"
In fact, sustainability disclosure is not merely a regulatory requirement—it's closely tied to market competitiveness, capital access, brand image, and global supply chain resilience. Below we summarize perspectives from regulations, stakeholders, capital markets, and corporate competitiveness to help you quickly understand why enterprises must invest in sustainability disclosure.
From Regulations to Markets: ESG Disclosure and Carbon Inventory
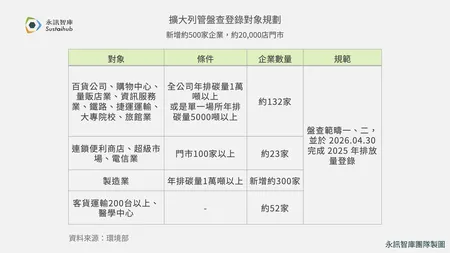
1. International Frameworks Are Rapidly Evolving—Disclosure Requirements Are No Longer Voluntary
With the implementation of IFRS S1/S2, CSRD (EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive), and GRI 2021 updates, the world is moving toward more consistent and comparable sustainability information disclosure.
These international trends are increasingly affecting Taiwan enterprises, for example:
- Supply chains requiring upstream carbon and ESG data
- Brand owners demanding compliance with specific standards (such as ESRS, SASB indicators)
- ESG performance evaluation becoming standard in sustainable procurement
What was once considered "voluntary" is now becoming essential capabilities for enterprises.
Source: Gemini
2. Market-Driven: Obtaining Certifications, Improving Bidding Power, Expanding Markets
For many B2B enterprises in manufacturing, technology, and food industries, ESG performance has become crucial for winning orders. For example:
- Sustainable procurement scores affect supplier qualification
- Carbon emission data influences contract renewals with multinational corporations
- Obtaining international certifications (such as ISO, product carbon footprint) directly enhances pricing power
In other words, meeting ESG disclosure requirements directly improves market competitiveness, especially when competing for international enterprise orders.
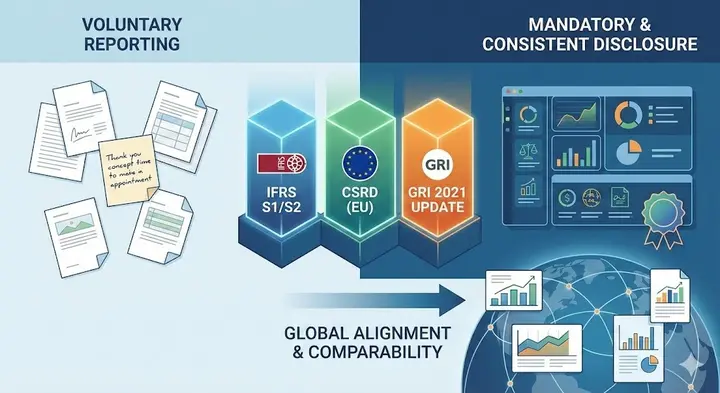
3. Capital Side: Investors and Banks Are Watching ESG
In recent years, banks, venture capital, CVCs, and even policy banks have incorporated ESG into:
- Financing and credit conditions
- Preferential loan rates (ESG-linked loans)
- Investment scoring (ESG rating) screening factors
Source: Gemini
The higher the transparency of sustainability disclosure, the clearer investors can understand the company's governance and risk management capabilities, thereby increasing trust.
Therefore, ESG is not just about brand image—it's an important ticket for enterprises to access capital.
Complete Guide to ESG Disclosure and Carbon Inventory: What Exactly Do Enterprises Need to Do?
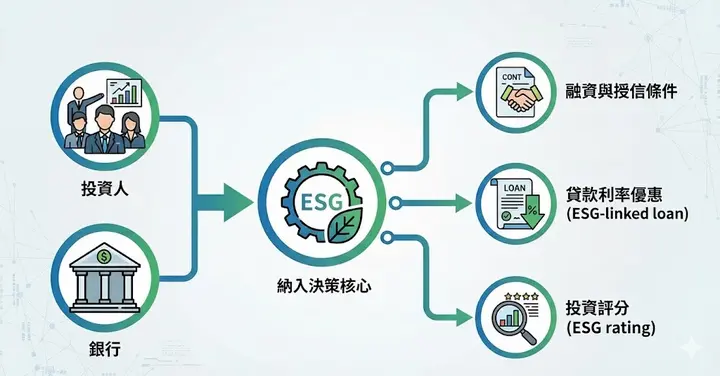
First, taking the annual sustainability report that most enterprises must complete as an example, it typically includes the following complete process:
1. Materiality Assessment
Based on the company's operations and stakeholder expectations, identify which issues need to be managed and disclosed.
2. Collecting Key ESG Data
Cross-departmental collection of environmental, social, and governance data, such as:
- Environmental: Energy, water, waste, greenhouse gases
- Social: Employee benefits, occupational safety, training
- Governance: Board composition, internal controls
3. Writing the Sustainability Report
Following GRI, IFRS S1/S2, or other frameworks to write annual disclosure content.
4. External Assurance and Stakeholder Communication
Assurance providers need to review extensive original documents and data to confirm whether disclosures are accurate.
5. Continuous Improvement and Long-term Strategy
Identify management gaps based on annual data and set next-step sustainability KPIs.
Carbon inventory, unlike sustainability reports, is typically a separate but highly important work item, including:
- Original data collection (water, electricity, natural gas, commuting, vehicles, equipment, etc.)
- Data compilation and emission calculation (based on emission factors)
- Inventory and report generation
- Improvement plans and carbon reduction pathway development (Net Zero / SBTi)
This data needs to be tracked annually, and most enterprises require "external assurance."
Source: Gemini
Four Major Pain Points Enterprises Commonly Face in ESG Disclosure and Carbon Inventory
Although the processes for sustainability reports and carbon inventory seem clear, enterprises often encounter the following issues in practice:
1. Cross-departmental Data is Scattered and Difficult to Collect
Procurement, administration, HR, engineering, accounting... information is scattered, and each collection feels like "starting from scratch."
2. Inconsistent Indicator Standards
Different frameworks have different requirements, including:
- GRI (International mainstream sustainability reporting standard)
- IFRS S1/S2 (Global financial and sustainability integration standard)
- TCFD (Climate risk)
- Carbon inventory standard differences (ISO 14064 / GHG Protocol)
Multiple standards easily cause interpretation confusion and gaps.
3. Data Duplication, High Error Rates, Difficult Version Management
Too many Excel versions, inconsistent cross-departmental files—errors are more likely during assurance.
4. Insufficient ESG Dedicated Personnel
Many companies still have administrative or accounting staff handling sustainability work part-time, leading to heavy burdens and low efficiency.
From Excel to Automation: How Digital Tools Help Enterprises Improve ESG Disclosure Efficiency
Facing increasingly large data volumes and stricter requirements, enterprises are gradually transitioning from Excel to ESG digital tools, mainly because:
- Automated data collection: Cross-departmental system-based reporting reduces manual processing.
- Reduced error rates: Systems can set logic checks and perform review management.
- Unified framework management: Complete alignment with GRI / IFRS / SASB indicators.
- Improved assurance efficiency: Systems maintain complete audit trails and evidence, eliminating concerns about assurance and audits.
After implementation, many enterprises have shortened data collection time from 2-3 months to weeks or one month, while significantly reducing data collection, compilation, and assurance pressure.
Practical Case: How Digital Tools Simplify Sustainability Report Processes
In the article From Pain Points to Breakthroughs: How Generative AI and Digitalization Improve Sustainability Report Efficiency, we approached from generative AI and digital tools perspectives, explaining how technology simplifies and improves sustainability report efficiency.
This time, we approach from practical scenario perspectives to understand how digital tools simplify sustainability report work items.
Facing the above issues of cross-departmental data collection, repeated collection, and inconsistent standards, the most common client request is "information integration"—hoping through one-time data collection and complete information gathering to avoid repetitive data exchanges, which increase workload while also raising error risks.
Syber Sustainability Management System connects data and reports through indicators, establishing data collection forms based on indicators. Users only need to fill in relevant information as instructed to complete information collection, reusable for multiple indicators and report responses.
Looking at benefits from practical cases, once users have completed greenhouse gas-related data collection forms, when the sustainability department links reports and data collection forms to GRI 305 indicators, the system can automatically import relevant information. The greenhouse gas data collection form can simultaneously correspond to other indicators (such as SASB, IFRS), and when writing related chapters, it can also be imported together.
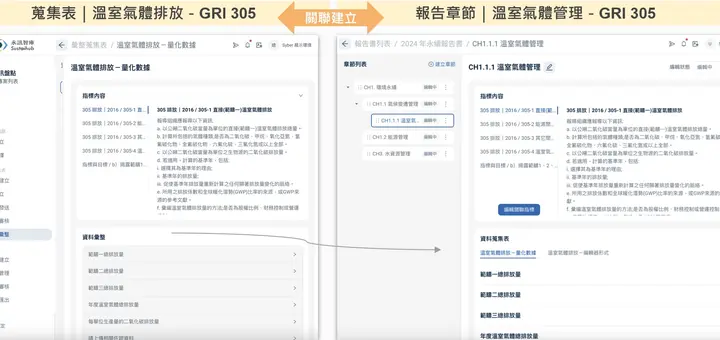
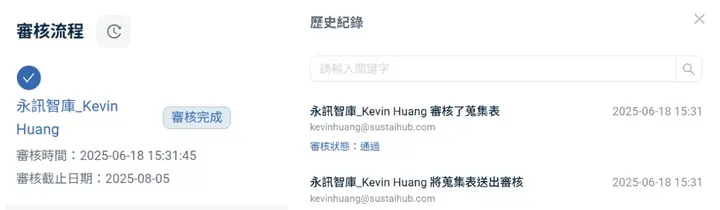
At the same time, the system maintains complete version records and audit trails, meeting related internal control and assurance requirements. When facing internal audits, regulatory spot checks, verification, or assurance requirements, there's no longer concern about missing audit trails.
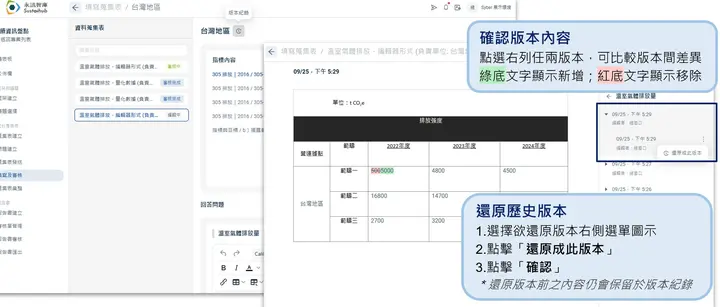
Note: System performs real-time editing records
Real-World Digital Tool Implementation: Understanding the Benefits from Carbon Inventory Work Sites
In our practical experience helping enterprises with carbon inventory, we often see that the most time-consuming and error-prone areas are not the calculations themselves, but collecting original data.
For most enterprises' current situations, whenever water, electricity, fuel, commuting, and equipment data are involved, the same problems always arise:
1. Complex Cross-departmental Data Collection, Scattered Excel Versions Difficult to Manage
Common situations include:
- One Excel for water bills, another Excel for electricity bills, each department providing different versions
- Administration, accounting, and engineering departments often don't know what data to provide
- Data formats from departments are inconsistent, with missing or incomplete items
- Uncertainty about which emission factors or formulas to apply, easily causing calculation errors
Consultants most often hear contacts say:
"I don't know what data to ask from departments, and they don't know how to fill it out."

Source: Gemini
2. Automated System Changes: What Data to Provide → The System Tells You Directly
After implementing carbon inventory digital tools, enterprises no longer need to fumble column by column in Excel. The system, following ISO 14064 / GHG Protocol logic, directly tells users:
- What original data needs to be filled (e.g., readings, usage, mileage, quantities)
- Which items need supporting documents
- What information is missing and needs supplementation
- After filling in data, the system automatically applies the latest emission factors
Thus enterprises go from "not knowing how to fill" to "just filling in actual numbers."
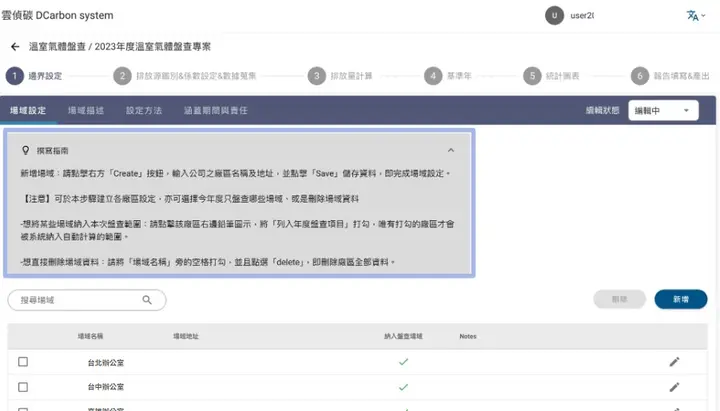
DCarbon System Guide: Provides filling instructions
3. Periodic Reporting, Less Likely to Miss Data
Traditional approaches often wait until year-end to start collecting data retrospectively, but information from the past 12 months is already scattered and hard to find.
Using a system is different:
- Get water and electricity bills monthly → Upload or report directly
- System automatically accumulates data needed for annual inventory
- No more year-end cleanup, avoiding missing data or lost documents
For coordinators, pressure is significantly reduced.
4. SMEs Especially Benefit: System Can Provide Suggested Inventory Items
Most SMEs don't have dedicated sustainability personnel, and many don't even know where to start with their first carbon inventory.
Therefore, in guiding enterprises, we've observed demand for suggested items. Currently, DCarbon can provide recommended greenhouse gas activity items based on industry, allowing enterprises to review and supplement data item by item according to system suggestions, accelerating the carbon inventory process.
5. Automated Report Generation: From Weeks to Hours
Traditional carbon inventory reports require multiple version consolidations, a complex process:
- Manual compilation of all data
- Calculating emissions
- Creating inventories and emission analyses
- Writing report content
Automated systems can:
- Generate inventories with one click
- Automatically produce inventory report drafts (including charts, emission structure, inventory boundaries)
- Each year only needs to update differential data, greatly improving efficiency
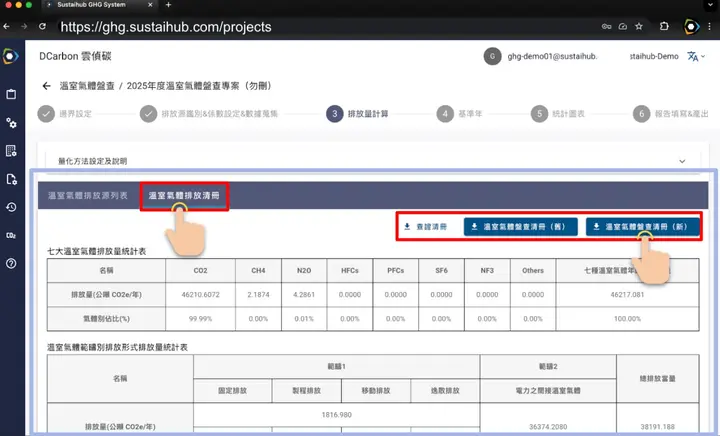
DCarbon System: One-click inventory generation
Digital Tools Have Become Core Capabilities for ESG Disclosure
From the above processes, pain points, and practical scenarios, we can see that sustainability disclosure complexity is rapidly increasing. Cross-departmental collection, framework comparison, data version control, and document management require substantial manpower and are prone to errors. After implementing digital tools, enterprises can not only shorten data collection and compilation time but also perform automatic checks based on standardized logic and systematically manage documentation, ensuring all information is accurate and traceable.
More importantly, digitalization can help enterprises gradually build a stable and scalable sustainability information foundation, including:
- Year-round cumulative data management, avoiding rush and gaps during annual settlement
- Automatic comparison with GRI / IFRS / SASB frameworks, reducing misinterpretation and duplication
- Essential audit trail preservation for assurance, improving assurance efficiency and credibility
- Automated chart and report generation, enhancing data presentation consistency
- Cross-year variance management, supporting long-term ESG indicator tracking
In the competitive era where sustainability management is transitioning from "must do" to "do well," digital tools are no longer just time-saving options—they are core capabilities supporting ESG disclosure quality, reducing compliance risks, and strengthening operational resilience. Only by building a reliable sustainability data foundation can enterprises gain true competitive advantage in international supply chains and capital markets.