What is CSRD? Why Are Companies Paying Attention?
CSRD, the full name being "Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive," is a new regulation proposed by the EU in 2021, replacing the original Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD). Through stricter regulations, this directive requires companies to disclose comprehensive ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) data to improve transparency and credibility.
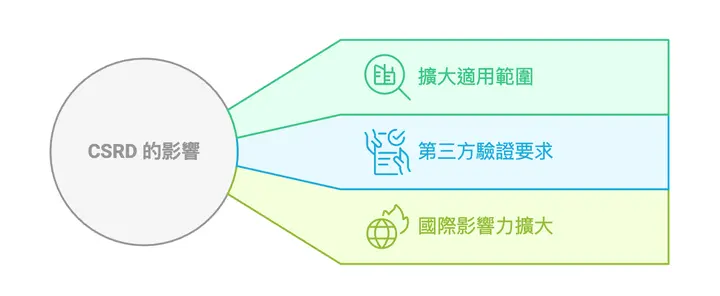
- Expanded Scope: Not limited to large enterprises; medium-sized or small enterprises in the supply chain may also be affected.
- Third-Party Verification Requirements: Companies must begin using limited assurance after October 2026; after October 2028, if deemed feasible, they must switch to reasonable assurance.
- Expanded International Influence: Besides local EU companies, it also affects international suppliers with business dealings.
Companies that cannot quickly adapt to these changes may face risks of brand reputation damage and loss of market access.
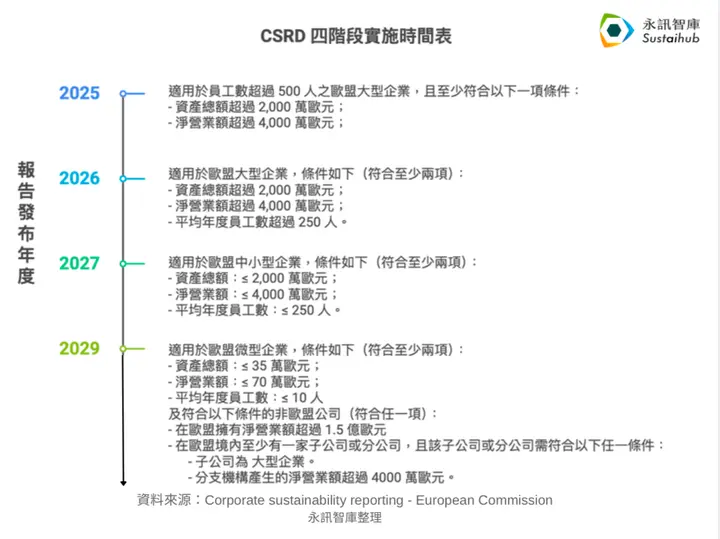
CSRD Four-Phase Implementation Timeline
CSRD implementation is divided into four phases, with companies of different sizes progressively required to disclose reports in accordance with CSRD. Starting from 2025, large enterprises must begin disclosing their 2024 sustainability reports; by 2029, micro-enterprises and some non-EU enterprises must also publish sustainability reports.
Below is the CSRD four-phase implementation table compiled by the Sustaihub consulting team:
What Are the CSRD Regulations?
CSRD regulations are based on the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), covering three main categories:
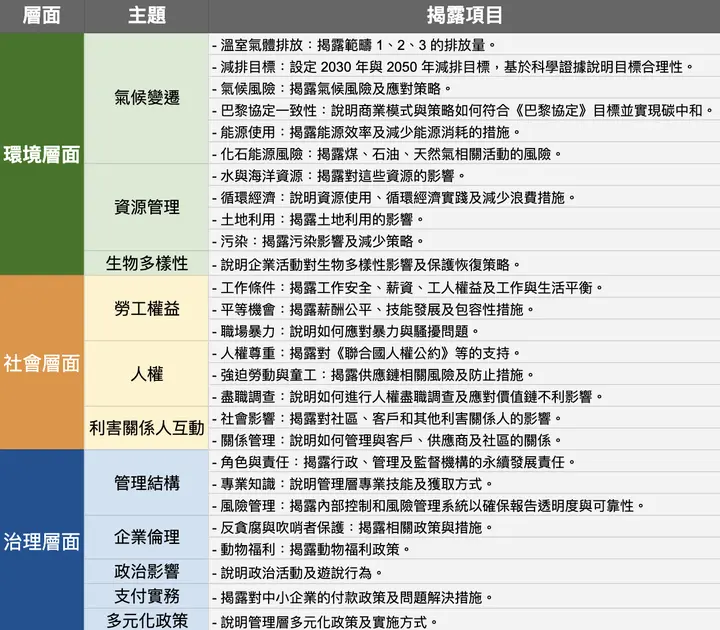
These requirements aim to increase corporate transparency and accountability in sustainable development. Companies need to comprehensively consider their environmental and social impacts and disclose relevant information to promote more sustainable business practices.
Major Challenges Facing Companies
With the official implementation of EU CSRD regulations, Taiwan companies in the supply chain are also required to provide compliant data due to the influence of EU customers. This makes companies face the dual challenges of low data integration efficiency and intensified supply chain management pressure:
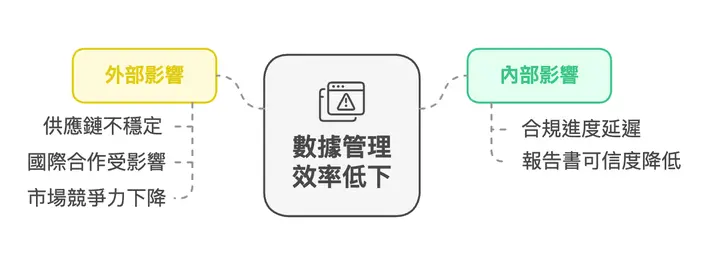
Challenge One: Difficult Information Integration, Scattered and Incomplete Data
Currently, ESG data in many companies is scattered across different departments, lacking a unified management approach. For example, carbon emission data is managed by the environmental department, while supplier data is held by the procurement department.
This scattered management approach faces the following problems when meeting CSRD's high-standard disclosure requirements:
- Difficult Compilation: Companies need to spend significant time searching for data across different departments and compiling it through traditional methods, with higher human error rates affecting data credibility and accuracy.
- Repeated Data Submission: Due to the lack of a unified data management mechanism, the same data may be repeatedly requested from internal responsible units, not only increasing workload but also affecting internal efficiency.
Challenge Two: Increased Supplier Management Requirements
CSRD requires large enterprises to disclose detailed supplier sustainability performance, creating pressure on Taiwan SMEs in the supply chain. For example:
- Higher Data Accuracy: Suppliers need to provide detailed carbon emission data, material sources, and other information, otherwise they may be considered non-compliant partners.
- Additional Audit Requirements: Each link in the supply chain may be required to submit supplementary data, increasing the burden on suppliers.
If companies in the supply chain cannot provide data that meets requirements, it may not only affect cooperation with core customers but may even force them to exit certain markets.
CSRD Launches First Batch of Reporting, How Should Companies Respond?
Method One: Improve Internal Data Integration Processes
- Unify Data Formats and Management Standards:
Unified ESG data templates and specifications ensure that data from different departments is consistent in format and easy to integrate, avoiding data contradictions due to format differences. - Combine Internal Control Mechanisms, Establish Multi-Level Review Processes
- Collection Phase: Departments conduct preliminary checks on data accuracy to ensure submitted data meets company standards.
- Disclosure Phase: Internal control audits are conducted before data disclosure to check whether CSRD requirements are met, reducing rejection risks.
Method Two: Strengthen Supply Chain Transparency
- Reference International Standards:
Organize data according to international standards such as GRI and ESRS to make data more credible. - Participate in Supply Chain Training:
Large enterprises provide CSRD data-related training for supply chain partners; actively participate to enhance internal understanding and execution capability of regulatory requirements.
Method Three: Adopt Digital Tools to Improve Efficiency and Transparency
Digital systems can solve data management challenges that companies face in the CSRD compliance process and provide the following benefits:
- Improve Data Accuracy: Record data change history to ensure all submitted data quality is more stable and reliable.
- Accelerate Data Integration: Centrally manage scattered information to shorten report preparation time.
- Reduce Manpower Burden: Automated project management processes reduce repetitive work, allowing teams to focus on sustainability strategies.
Sustainability Management System Case Study
Sustaihub Syber Sustainability Management System has three key features that help companies ensure the accuracy of sustainability information:
- History Records, Review Processes, Multi-Level Permission Controls: Improve Data Reliability
- Cross-Department Data Compilation, Solve Data Fragmentation Issues: Accelerate Data Integration
- Automated Project Management and AI Collaboration Integration: Reduce Manpower Burden
Through the Syber Sustainability Management System, companies can achieve compliance and improve internal efficiency without consuming significant manpower and time, providing comprehensive support for sustainable development. It is the best sustainability report collaboration platform for enterprises.






