What is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
Corporate Social Responsibility, abbreviated as CSR, refers to the requirement for enterprises to balance public social interests while contributing to economic development and pursuing profits. This includes continuous compliance with ethical and legal norms regarding the rights and interests of corporate stakeholders—including employees, customers, suppliers, investors, and local communities—while striving to improve employee welfare and the quality of life for communities, society, and the environment.
Taiwan first introduced the CSR concept when the Taiwan Stock Exchange published the "Corporate Social Responsibility Best Practice Principles" in 2010. This law was renamed to "Sustainable Development Best Practice Principles for TWSE/TPEx Listed Companies" in December 2021. Article 2 states: "To encourage TWSE/TPEx listed companies to actively practice sustainable development in their business operations, comply with international development trends, improve employees', communities', and society's quality of life through corporate citizenship, and promote competitive advantages based on sustainable development." This fully expresses the importance of CSR to enterprises. For those interested in researching CSR or responsible for writing corporate sustainability reports in the future, this guideline is highly recommended essential reading—it's very easy to understand.
What is ESG Sustainability? Understanding the 3 Key ESG Indicators
ESG is an acronym for Environmental, Social, and Governance. These three dimensions were mentioned in a 2005 United Nations report as data and evaluation indicators for corporate operations, serving as important information for external investors to reference regarding corporate sustainable management and investment decision evaluation.
According to the GRI (Global Reporting Initiative) Standards, the three ESG dimensions cover the following content for quick understanding:
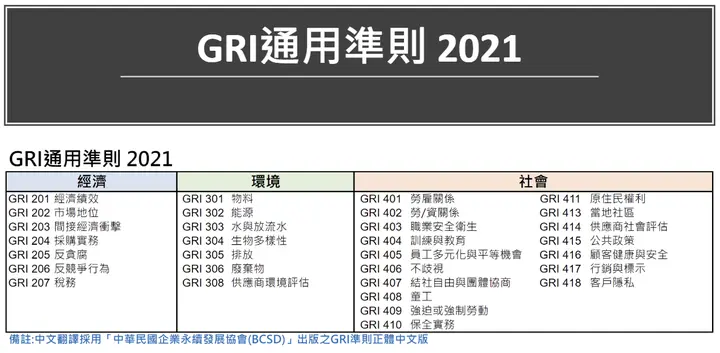
What's the Difference Between CSR and ESG?
CSR encompasses environmental protection, social responsibility, and corporate governance, as well as local revitalization, local investment, and sustainability activities. However, to facilitate understanding and measurement of corporate social responsibility by enterprises, investors, and the public, ESG indicators were developed. By proposing clear specifications for "Environmental Protection," "Social Responsibility," and "Corporate Governance," ESG provides guidelines for enterprises to follow, becoming a reference for measuring whether companies fulfill their corporate social responsibility. Simply put: CSR is like a large garden, and ESG is one of the gardener's tools for regularly or irregularly inspecting the garden's actual operations and continuous growth or areas needing improvement.
Additionally, as international investors and industry chains increasingly focus on ESG-related issues, Taiwan's Financial Supervisory Commission released the "Corporate Governance 3.0 - Sustainable Development Roadmap," which requires ESG information disclosure and references to international standards, including TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures) to link climate risks to corporate governance, and SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board) for material financial information and investment decisions. This not only increases sustainability report transparency but also provides reference for investor decision-making.
Why Should Enterprises Focus on ESG? 4 Key Reasons for Sustainable Development

Having analyzed the differences between CSR and ESG, here are 4 key reasons why they are increasingly valued by all parties.
ESG Importance 1: Compliance with Government Regulations
The Financial Supervisory Commission's "Corporate Governance 3.0 - Sustainable Development Roadmap" requires that from 2023, all listed companies with capital of NT$2 billion or more must prepare sustainability reports (ESG Reports) using the international GRI Universal Standards framework (updated from 2016 to the 2021 version), referencing SASB (Sustainability Accounting Standards Board) to address investor concerns about industry issues, and disclosing TCFD (Climate-related Financial Disclosures) to address climate change risk response measures to stakeholders.
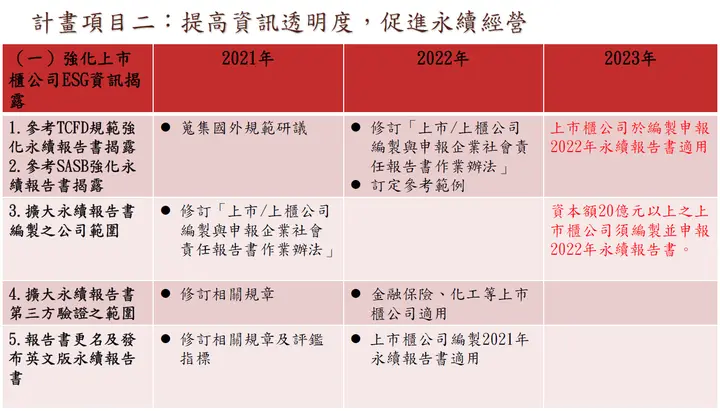
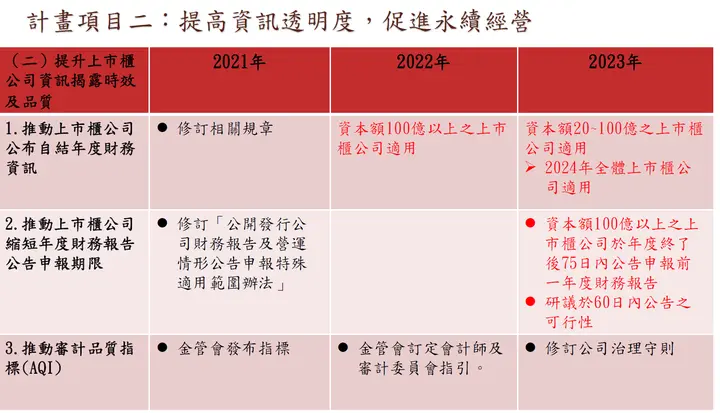
Source: Taipei Exchange - Corporate Governance 3.0 Sustainable Development Roadmap Presentation
ESG Importance 2: Attracting Investor Interest
The investment community has gradually become aware of threats from external factors such as climate change. Currently, about 44% of banks in Taiwan have signed the Equator Principles (EPs)*Note 1, a set of principles for measuring and managing social and environmental risks. Besides environmental concerns, COVID-19 has also stimulated more scrutiny of social and governance issues, accelerating investors' attention to corporate ESG performance for sustainable investment considerations. Under this wave of sustainability focus, preparing sustainability reports not only allows employees, shareholders, and stakeholders to clearly understand company operations but also enables investors to learn about the company's financial situation and operational policies. Enterprises that treat consumers, employees, and the environment well can demonstrate "giving back to society," making them more likely to gain public and investor favor.
*Note 1: Calculated based on FSC Banking Bureau official website statistics as of June 15, 2022
ESG Importance 3: Enhancing International Competitiveness
Many enterprises are often required by international customers to provide corporate sustainability reports (ESG Reports), as these reports disclose ESG indicators, SASB, TCFD, and other practices. Customers can understand whether enterprises are fulfilling their corporate social responsibility in human rights policies or environmental protection, making them more willing to accelerate cooperation or increase procurement and transaction amounts. Well-known companies like Apple and Google all value sustainability report content. Additionally, government corporate governance evaluations encourage companies to publish English versions of sustainability reports, further promoting international alignment and allowing global customers and investors to learn about corporate sustainability practices, bringing more cooperation opportunities and operational performance.
ESG Importance 4: Reducing Climate Change Risks
When assessing climate change risks, enterprises evaluate significant impacts that events such as fires, floods, and droughts may have on operations, establish corresponding policies and risk prevention management in advance, enhance corporate resilience to climate change, and immediately activate emergency response plans. These are simultaneously disclosed in sustainability reports to provide stakeholders with understanding of business risks and related measures.
How Should Enterprises Implement ESG? Understanding Key Considerations and Applications
Sustainability reports are a medium for enterprises to communicate with stakeholders. Disclosing ESG practices and performance in reports not only gains investor trust but also allows enterprises to conduct self-assessment for continuous improvement. However, it should be noted that simply publishing a sustainability report does not mean ESG is implemented—actual corporate practices are also indispensable key indicators.
For example, Starbucks insists on using fair trade coffee beans to avoid harming foreign workers' rights; Nike shoes are made from recycled waste materials, committed to maintaining a more environmentally friendly ecosystem; 7-ELEVEN and FamilyMart launched online surplus food maps, solving food surplus problems while allowing more people in need to access resources at more affordable prices.
Sustaihub Makes ESG Reports Accessible and Efficient, Fulfilling Corporate Social Responsibility
After this introduction, we hope you better understand the differences between ESG and CSR and the importance of ESG sustainability reports to enterprises. Want to create a sustainability report that records your company's internal ESG practices, regularly takes inventory, and provides stakeholders with continuous improvement references?
Sustaihub's Syber Sustainability Management System can help. Through cloud-based digital sustainability management, the system helps enterprises conduct data inventory, efficient collaborative editing, and progress management. The system is based on GRI 2021 Universal Standards, allowing relevant staff to use the CSR big data database to search global ESG report keywords, quickly view desired ESG data content and locate it in reports. This saves time and labor costs spent on Excel, Word, and email confirmations across departments, enabling more efficient information integration, sustainability report production, and related business decisions. For any operational questions, professional consulting teams are available to guide you in successfully fulfilling corporate social responsibility.
Apply for a trial now to experience Sustaihub's Syber Sustainability Management System's convenient services and feel a sense of work accomplishment.
Extended reading:
Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): Scenario Analysis and Climate-Related Issues
Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): Risks, Opportunities, and Financial Impacts

